Using Survival Models to Estimate Invertebrate Prey Identification Times in a Generalist Stream Fish
Abstract
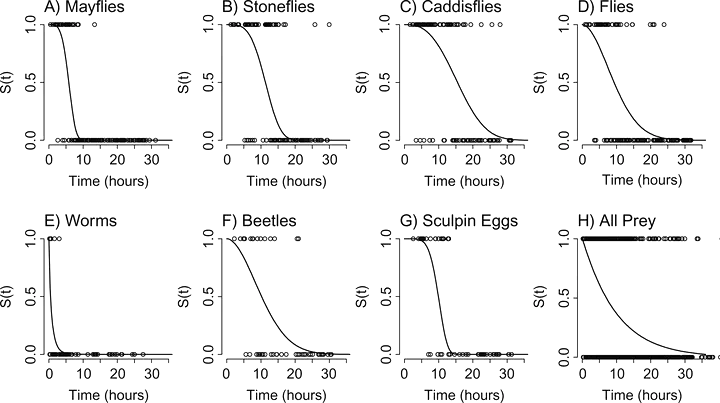
Estimates of predator feeding rates are important for understanding trophic dynamics. One common method for quantifying feeding rates in fishes combines mass‐based diet data with gastric evacuation times to estimate prey mass consumed per predator. An alternative approach is to estimate the rates of prey individuals consumed using prey identification time—the time period over which prey remain identifiable in a predator’s stomach. One challenge with the analysis of prey identification times, however, is that the response variable is likely to be censored because the “true” prey identification time cannot be observed directly. Here, we applied survival analysis that can incorporate censored data to estimate the effects of predator body size, water temperature, and prey characteristics (type, count, and body size) on identification times in Reticulate Sculpin Cottus perplexus. We focused on seven types of prey that are common in this generalist predator’s diet: mayflies (Ephemeroptera), caddisflies (Trichoptera), stoneflies (Plecoptera), true flies (Diptera), beetles (Coleoptera), worms (Annelida), and sculpin eggs. An information‐theoretic model comparison approach indicated that an accelerated failure time Weibull model with all five covariates provided the best relative fit to the full data set. Prey type had a strong effect on prey identification time, with annelid worms having the shortest times (<1 h) and caddisflies having the longest times (>15 h). Water temperature decreased prey identification time (7.5% per 1°C increase), whereas prey count (i.e., meal size) increased prey identification time (15.5% per additional prey item). Predator body size had a weak negative effect on prey identification time (0.04% per 1‐mm increase). Body sizes of some prey taxa, including mayflies, caddisflies, and stoneflies, increased prey identification times, leading to an interaction between prey type and prey size. Our study highlights the utility of survival analysis for quantifying variation in prey identification times in the diets of generalist predators.