Nestedness patterns and the dual nature of community reassembly in California streams: a multivariate permutation-based approach
Abstract
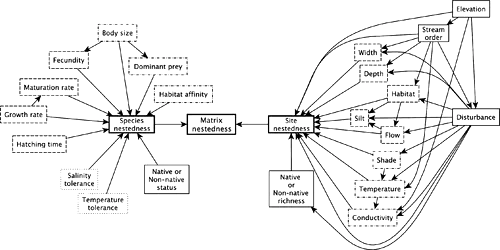
Many factors contribute to the nonrandom processes of extinctions and invasions that are changing the structure of ecological communities worldwide. These factors include the attributes of the species, their abiotic environment, and the interactions and feedbacks between them. The relative importance of these factors has been difficult to quantify. We used nested subset theory and a novel permutation‐based extension of gradient analysis to disentangle the direct and indirect pathways by which these factors affect the metacommunity structure of freshwater fishes inhabiting the streams tributary to the San Francisco Bay. Our analyses provide quantitative measures of how species and stream attributes may influence extinction vulnerability and invasion risk, highlight the need for considering the multiple interacting drivers of community change concurrently, and indicate that the ongoing disassembly and assembly of Bay Area freshwater fish communities are not fully symmetric processes. Fish communities are being taken apart and put back together in only partially analogous trajectories of extinction and invasion for which no single explanatory hypothesis is sufficient. Our study thereby contributes to the forecasting of continued community change and its effects on the functioning of freshwater ecosystems.